Third-Party Cookie Phase-Out: What Marketers Need to Know
Cookies are an essential part of internet usage, allowing websites to remember you and provide a more personalized experience. This browser-based technology can be used to identify a device or a specific user. Although primarily designed to streamline a user’s web experience, cookies also play an integral role in digital marketing. Tracking activity across the web like websites frequently visited, interests shown and purchases made gives marketers insight into consumer behaviors that can be used to build robust visitor profiles to improve ad targeting relevancy.
Cookies were never really meant to do as much work or contain and share as much information as they currently do. As a result, consumers have grown increasingly concerned about the privacy of their personal information and are demanding greater transparency, choice and control over how their data is used. This has become a driving force behind major players like Apple, Mozilla and Google modifying their support of the tracking technology, creating a need for digital advertisers to adapt with innovative solutions that do not rely on cookies.
But not all cookies are going away. First-party cookies will remain (at least for now). Potentially troubling third-party cookies are what will soon become obsolete. There is no reprieve. It’s coming and is unavoidable. The technology that provides the foundation for online marketing as we know it today will cease. So, what exactly does that mean for the advertising industry and your brand’s digital campaigns?
First-Party Cookies vs. Third-Party Cookies
Let’s start with a quick refresher on the difference between first-party cookies and third-party cookies. A first-party cookie is code generated by the website being used. In general, these are considered safe and allow the site to gather basic analytics about the user’s visit(s). The data is limited to the user’s behavior on that website; their activity on other websites not affiliated with that domain is not shared.
Third-party cookies are placed by another website that is not the website the user is browsing (hence the name third-party). These cookies track a visitor’s activity as they browse the web collecting information like sites visited and even potentially contact information like name, email address, street address and phone number.
This data is used to help understand a user’s interests, preferences and traits allowing brands to target more effectively based on that information. Third-party cookies also enhance attribution capabilities by providing a more holistic view of what goes into a conversion which facilitates campaign optimization.
Data Privacy Concerns
Until recently, most users didn’t realize they were being tracked by third parties and the depth of information collected. In an effort to promote data privacy, major browsers either already are or will soon significantly limit both the persistence and utilization of third-party cookies.
A series of laws and government regulations designed to protect user information have evolved over time as well. The two most significant policies worldwide are the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). GDPR was designed to protect the personal information of users in the European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA) while CCPA gives consumers in California more control over the personal information a business collects about them. Voters recently approved Proposition 24, the California Privacy Rights and Enforcement Act (CPRA). It amends key elements of the CCPA and will replace it effective 2023.
As a result, some companies have chosen to implement permission-based third-party cookies, while others have begun to phase them out completely and are seeking new solutions. Regardless, third-party cookies are living on borrowed time challenging marketers to find an alternative that balances consumer privacy and personalization.
Third-Party Cookie Phase-Out
Apple Safari and Mozilla Firefox already block all third-party cookie tracking on their browsers. Although Google has now postponed removing support of third-party cookies on Chrome, the three-month phase-out period is expected to be complete by late 2023.
As of Q2 2020, the top three desktop web browsers, Chrome, Safari and Firefox held 68.3 percent, 9.3 percent and 8.9 percent of the market share respectively. In terms of mobile browser traffic, Chrome held 61.9 percent and Safari held 26.9 percent of the market share as of June 2020. Consequently, Chrome’s removal of third-party cookies will have the strongest impact on the advertising industry to date.
Then there’s the mobile app world where IDFA (Identifier for Advertisers) is used to track user behavior. This randomly generated and generally anonymous identifier enables addressable advertising and conversion tracking online. Apple dealt a crushing blow to this technology with its iOS 14.5 launch in April 2021 by disabling it by default. Originally scheduled to go into effect with the release of iOS 14 in September 2020, the delay gave partners a brief reprieve. However, users are now required to opt-in before apps can collect and share data using the device identifier. Despite an ad campaign in defense of the personalization enabled by this tracking, Facebook was forced to comply and request permission to track user activity beyond the app.
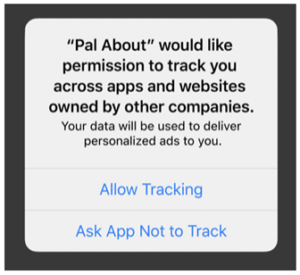
Since the iOS 14.5 release, users can configure data privacy settings with one tap.
Advertising Implications
So, what does this mean for your brand’s digital advertising campaigns? It’s an end to current cookie-based targeting and measurement across the digital ecosystem that provides insight into which channels, creative, messages and placements deliver the best ROI. Although the loss of third-party cookies doesn’t mean this ability is gone forever, it does make tracking and performance measurement more challenging.
It’s important to note the change will have a limited impact on advertising within large platforms like Google, Facebook, Microsoft and Pinterest. These walled gardens where users log in to accounts and accept detailed terms and conditions around data usage can still collect data from users and easily advertise within their own domain without much restriction. However, once a visitor navigates off these platforms, standard privacy restrictions apply.
A Replacement for Third-Party Cookies
Discussions are underway among various industry bodies such as the IAB and key stakeholders to develop new technical standards and guidelines. Although independent ad tech firms are working feverishly to develop their own solutions, all eyes are on Google for a new standardized replacement.
Google has, in fact, has been working on an alternative solution called the Privacy Sandbox that would curtail improper tracking while continuing to allow ad targeting within the Chrome browser. It seeks to strike a balance between personalization and privacy by anonymously aggregating user information and keeping more of it on the device itself rather than storing it in the cloud. As a Google Premier Partner, Mindstream Media Group has access to resources to keep us on top of developments like this that will impact our clients’ current and future campaigns.

Source: Google
Apple has a solution as well that was actually released in 2018 and is now experiencing increased adoption since iOS 14.5. The SKAdNetwork, or simply “ad network API,” is an integration between advertising platforms and Apple’s App Store that attributes mobile app installations and post-install activity to advertising campaigns in a privacy-compliant manner. However, it comes with its own challenges – namely, it aggregates users and is not delivered in real-time, complicating attribution and optimization.
Facebook has released an updated version of the Facebook SDK to provide support for Apple’s SKAdNetwork API. However, because of its heavy dependence on app advertising, these changes have had a significant impact on Facebook’s Audience Network.
Targeting Alternatives
Although third-party cookies have become a pillar for behavioral targeting, it’s important to remember that is just one targeting option. Viable alternatives include the following:
- Focus on first-party data.
Leverage your brand’s customer data platform (CDP) to get to know who your customers really are and target them directly. Because the data collected is more personalized than third-party cookies, this option can generate even better sales and conversions.
- Establish a direct partnership with publishers.
“As third-party data disappears with cookies and GDPR compliance, publisher audience knowledge is now being seen as a viable data source for segmentation and targeting and deeper insights in audience and brand engagement,” says Damon Reeve, CEO at The Ozone Project.
- Optimize retargeting and owned media.
Upload your own contact list to a platform such as a social media network or search engine to enable targeting to those contacts or a mirror audience that shares similar demographics. Owned media, such as websites and social platforms, should also be strengthened to engage visitors tapped through retargeting efforts.
- Utilize contextual targeting.
Contextual methods that reach consumers at key moments of research and inspiration will not be affected since they broadly target device type, brand, operating system or mobile carrier. This option also provides control over the type of content the ad will run adjacent to such as Health, News or Sports and includes parameters for geography and time of day.
The ability to track, measure and target across sites, screens and channels is imperative to crafting efficient and effective media strategies. Although a radical shift, the phase-out of third-party cookies could open the door to entirely new methods we have yet to imagine and create a more engaging, fraud-limited environment.
We view this change as an opportunity to reach an audience that chooses to see our clients’ ads by the nature of opting-in to tracking within apps they find valuable and trustworthy. The publishers and apps we partner with can distribute – and limit – content, features and ads based on an individual’s opt-in settings, involving the user in an unprecedented tracking relationship, a deeper level of trust and an enhanced online advertising experience.
Now more than ever, agile marketing strategies are a must. Connect with us to learn how we can Fast-Forward Your Business and deliver meaningful progress on your goals amidst the continual evolution of digital media.
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in February 2021 and has been updated for freshness and accuracy.
More from Mindstream Media Group

Meet the Mindstreamer – Chandler Swanner
Chandler Swanner’s interest in advertising dates back to her childhood. Her mother (and role model in life) was a Media […]

Meet the Mindstreamer – Kaya Bucarile
She plans and oversees media strategy for agency clients, working closely with project and platform managers to ensure that we […]

Advertising to Teens: How Brands Can Connect with a Generation that’s Always on Their Phones
Ask any parent and they’ll tell you, teens are almost always on their phones. According to Common Sense Media, 78 […]
