Since its inception in 2008, Moz’s Local Search Ranking Factors survey has been the go-to guide for digital marketers and local businesses looking to increase their rankings in Google’s local search results.
Each year the survey asks various industry experts to share what they think are the most influential ranking factors in local search results based on their experience with Google’s search engine results pages (SERPs) and algorithms. The survey is broken out into two main sections:
- Local pack ranking factors (elements that affect search results that appear in the local 3-pack/snack pack).
- Localized organic ranking factors (elements that affect organic search results for local business websites).

The survey includes the top 50 ranking factors for each section and groups various ranking factors into thematic categories. The survey also includes the top foundational and top competitive factors to provide insight into what businesses need to do to get listings ranked in the first place, and what can be done to out-rank competitors.
Local pack ranking factors
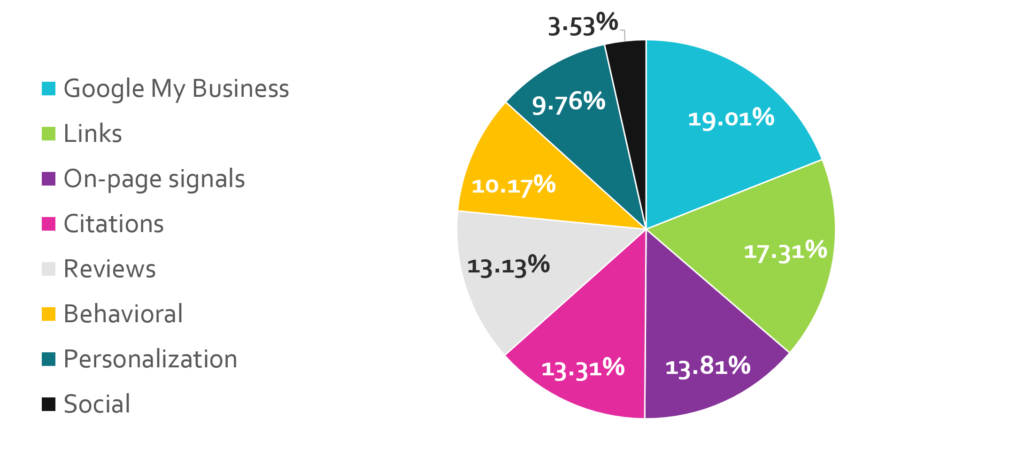
Compared to last year, this year’s survey revealed a shift in the thematic factors that affect search results in the local pack. Google My Business (GMB) signals, such as proper business category associations, are still the most influential group of ranking factors; but, their importance decreased slightly from last year.
As GMB signals dipped, review signals increased in importance over the past year. These shifts suggest that Google is rewarding businesses who have a higher quantity and variety of reviews and that properly setting up your GMB account is still crucial if you want to rank in the local pack.
The most notable shift in local pack ranking factors this year was link and citation signals. This year, link signals took over as the second most important group of ranking factors, whereas last year citation signals held this spot. Citation building is still essential to a successful local SEO campaign but the focus is shifting from quantity/authority of structured citations to quality structured citations on the primary data sources (the four main data aggregators) and tier 1 data sources (major search engines and local directories).
Moz’s top 10 local pack ranking factors
- Proximity of Address to the Point of Search
- Physical Address in City of Search
- Proper GMB Category Associations
- Quality/Authority of Inbound Links to Domain
- Consistency of Citations on the Primary Data Sources
- Domain Authority of Website
- Product/Service Keyword in GMB Business Title
- Quality/Authority of Structured Citations
- Consistency of Citations on Tier 1 Citation Sources
- Click-Through Rate from Search Results
Local organic ranking factors
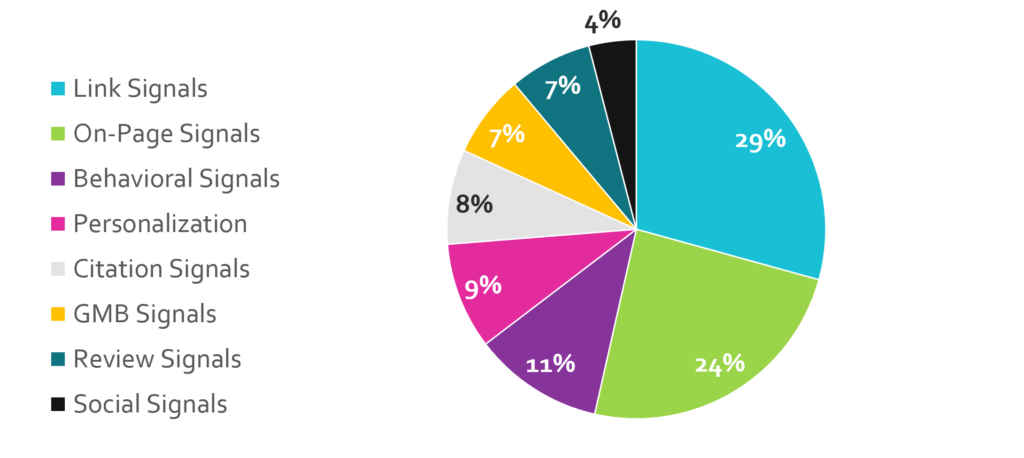
Ranking signals for localized organic search results did not see as big of a shift this year as local pack signals. Similar to the previous year, signals were the most influential category of ranking factors in 2017. In fact, “Quality/Authority of Inbound Links to Domain” surpassed “Domain Authority” as the No. 1 ranking factor for localized organic results.
“Diversity of Inbound Links to Domain” and “Quantity of Inbound Links to Domain” also increased in importance over the past year as both factors are now in the top five most influential ranking factors. Over the past few years, the survey’s results indicated that Google is putting more weight on inbound links. This year’s survey solidifies this trend as five of the top 10 factors impacting localized organic results are related to inbound links.
Similar to the results for the local pack ranking factors, citation signals decreased in importance for localized organic results in this year’s survey. All ranking factors related to citations moved down on the organic list as the focus also shifted to quality of structured citations on the primary data sources and tier 1 data sources.
Another notable shift in ranking factors for localized organic results is the decrease of importance placed on factors that focus on geo-modifiers on the site. For instance, “City/State in GMB Landing Page Title” and “City, State in Most/All Website Title Tags” both fell out of the top 10 most influential ranking factors, with each factor dropping at least 10 positions. This shift reinforces the notion that simply adding geo-modifiers to your site will not suddenly increase rankings for local search results.
Moz’s top 10 organic ranking factors
- Quality/Authority of Inbound Links to Domain
- Domain Authority of Website
- Diversity of Inbound Links to Domain
- Topical (Product/Service) Keyword Relevance of Domain Content
- Quantity of Inbound Links to Domain
- Quantity of Inbound Links to Domain from Locally-Relevant Domains
- Click-Through Rate from Search Results
- Geographic (City/Neighborhood) Keyword Relevance of Domain Content
- Product/Service Keywords in Anchor Text of Inbound Links to Domain
- Mobile-Friendly/Responsive Website
Need help managing your brand’s local listings? Contact Mindstream Media Group to learn more about our Location Services.